OAuth2
This module performs authentication using an external OAuth provider.
The current supported authentication flows are:
- Confidential Authorization code.
- Public Authorization Code.
Confidential
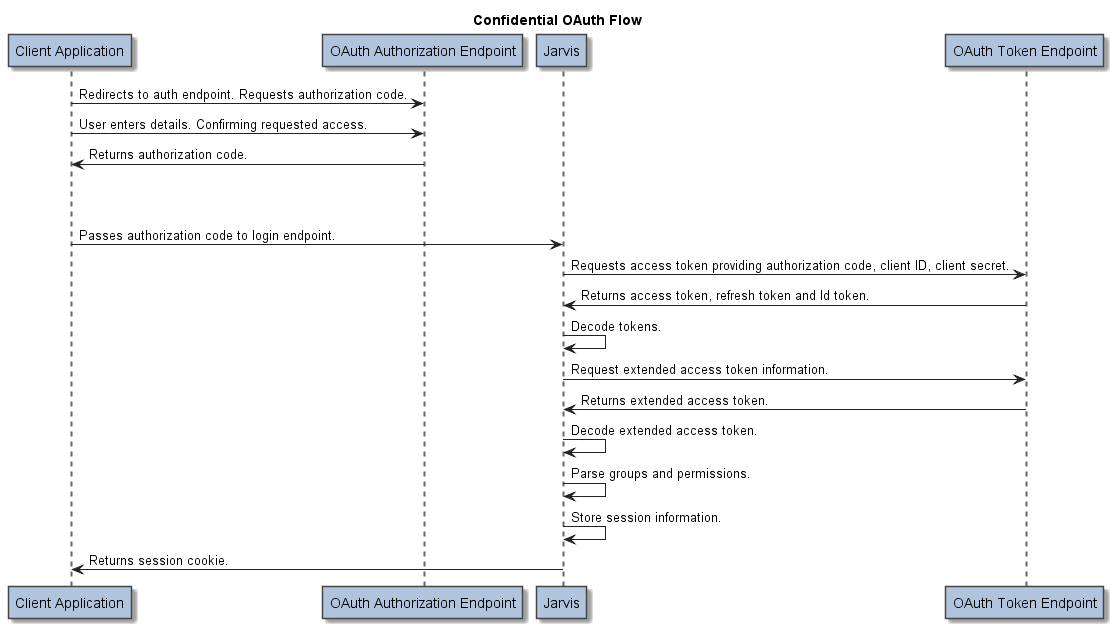
The Jarvis OAuth2 confidential access type is a variation on the standard single page application Authorization Code Flow grant mechanism. For more information see: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory-b2c/authorization-code-flow.
Confidential flows expect a single page application to pass the authorization code passed from the authentication provider back to Jarvis. Jarvis will use this information to request the access, id and refresh tokens on behalf of the application using an additional secret key for added security.
Jarvis is responsible for parsing the received token, storing user and group information and binding it against the session cookie associated with the requesting client.
Example:
<jarvis>
<app>
<login module="Jarvis::Login::OAuth2">
<parameter name="grant_type" value="auth_code"/>
<parameter name="access_type" value="confidential"/>
<parameter name="client_secret" value="<client_secret>"/>
<parameter name="client_id" value="<client_id>"/>
<parameter name="site" value="<base_oauth_site_path>"/>
<parameter name="token_path" value="/oauth2/token"/>
<parameter name="logout_path" value="/oauth2/logout"/>
<parameter name="self_signed_cert" value="<option_pem_file_path>"/>
<parameter name="redirect_uri" value="<application_redirect_uri>"/>
<parameter name="ssl_opts" value="SSL_hostname=nsquared.nz"/>
<proxies>
<proxy scheme="http,https" proxy_url="http://10.10.10.100:8080"/>
<proxy scheme="ftp" proxy_url="http://10.10.10.200:8080"/>
</proxies>
</login>
...
The parameters are:
| Attribute | Default | Notes |
|---|---|---|
grant_type |
(none) | [Required] The type of OAuth grant type to request. Must be auth_code for confidential authorization flow types. |
access_type |
(none) | [Required] The type of authorization flow to use. Must be “confidential” for confidential authorization flow types. |
client_id |
(none) | [Required] The ID of the client that is being used to perform our OAuth request. |
client_secret |
(none) | [Required] The secret associated with the client that is being used to perform our OAuth request. |
site |
(none) | [Required] The base path of the OAuth endpoint. This will be used as the base for constructing any requests that are sent to the OAuth endpoint. |
token_path |
(none) | [Required] The path appended to the site that will form the URI that is used to retrieve a valid access token from a provided authorization code. |
logout_path |
(none) | [Required] The path appended to the site that will form the URI that is used to invalidate a previously authenticated access token and logout from an external OAuth provider. |
self_signed_cert |
(none) | In some cases an OAuth provider may be operating under SSL using a self signed certificate. Normally Perl would reject these as insecure however if provided Jarvis will attempt to load the self signed certificate in order to trust the SSL session. |
redirect_uri |
(none) | [Required] The URI that is used by the OAuth endpoint to determine where to redirect the traffic towards. This must be the same as both the calling application and the OAuth provider. |
ssl_ops |
(none) | Additional arbitrary options to be provided to the SSL layer, in key=value pairs separated by pipes, e.g. a=1|b=2Refer to the documentation for the Perl module LWP::UserAgent and IO::Socket::SSL for details of the available keys. |
proxies |
(none) | Definition of proxies to be used for requests to the endpoint, with each entry specified with a “proxy” entry containing a comma separated list of schemes (if applicable) and a proxy_url. Refer to the documentation for the Perl module LWP::UserAgent for more details of the available schemes. |
Public
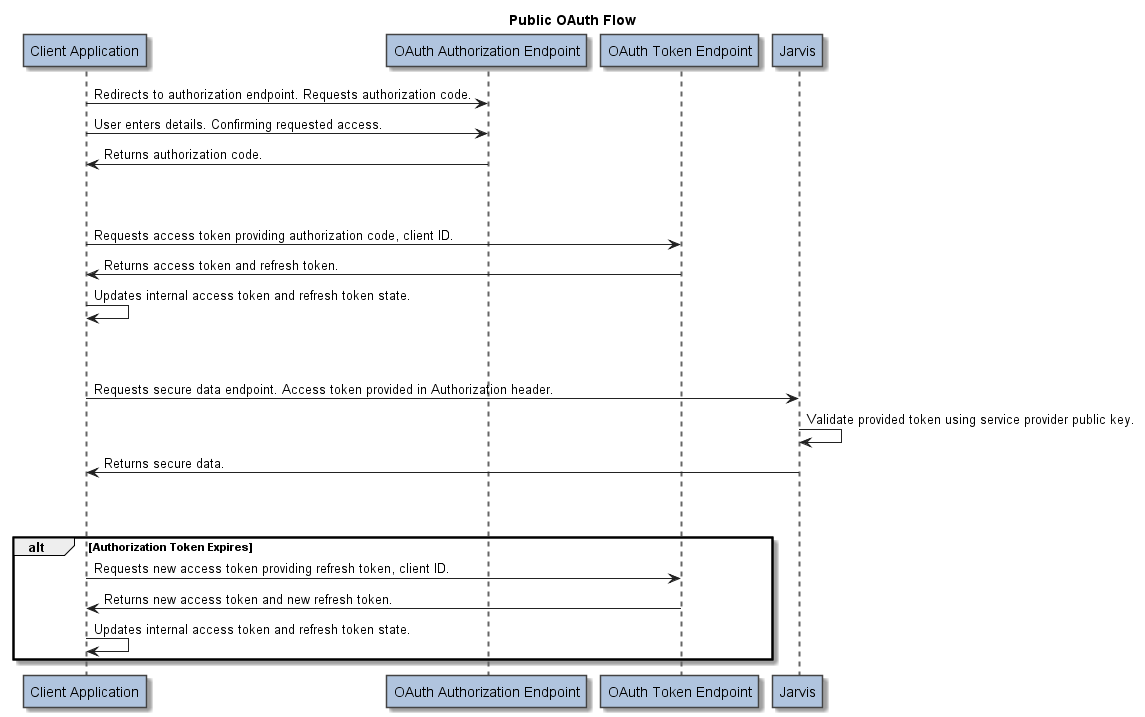
The Jarvis OAuth2 public access type heavily takes influence from the standard Authorization Code Flow grant mechanism. For more information see: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory-b2c/authorization-code-flow.
Public flows expect a single page application to perform the initial authorization step and token exchange, subsequently providing the access token to the back-end via an Authorization Bearer header for each request requiring access to secure resources.
Jarvis is responsible for parsing the provided token, validating it against an available public key endpoint and extracting user and group information as required.
Example:
<jarvis>
<app>
<login module="Jarvis::Login::OAuth2">
<parameter name="grant_type" value="auth_code"/>
<parameter name="access_type" value="public"/>
<parameter name="site" value="<base_oauth_site_path>"/>
<parameter name="public_key_path" value="/<realm>/discovery/v2.0/keys"/>
<parameter name="public_key_store" value="/tmp/auth_public_key"/>
<parameter name="public_key_lifetime_seconds" value="600"/>
<parameter name="groups_key" value="groups"/>
<parameter name="username_key" value="unique_name"/>
<parameter name="user_identifier_key" value="oid"/>
<parameter name="self_signed_cert" value="<optional_pem_file_path>"/>
</login>
...
When running under web environments such as Apache considerations will need to be made when handling Authorization Bearer tokens.
By default Apache will not forward Authorization headers. This can be enabled by adding the following to site the relevant site configuration:
SetEnvIf Authorization "(.*)" HTTP_AUTHORIZATION=$1
The parameters are:
| Attribute | Default | Notes |
|---|---|---|
grant_type |
(none) | [Required] The type of OAuth grant type to request. Must be auth_code for public authorization flow types. |
access_type |
(none) | [Required] The type of authorization flow to use. Must be public for public authorization flow types. |
site |
(none) | [Required] The base path of the OAuth endpoint. This will be used as the base for constructing any requests that are sent to the OAuth endpoint. |
self_signed_cert |
(none) | In some cases an OAuth provider may be operating under SSL using a self signed certificate. Normally Perl would reject these as insecure however if provided Jarvis will attempt to load the self signed certificate in order to trust the SSL session. |
public_key_path |
(none) | [Required] The path appended to the site that will form the URI that is used to request the public key information from an external OAuth provider. |
public_key_store |
/tmp/auth_public_key |
The path and filename used to store the parsed public key from the external OAuth provider. This is utilized for caching to avoid additional requests to the external OAuth provider. |
public_key_lifetime_seconds |
600 |
The total lifetime of the cached public key store file before fetching an updated key from the external OAuth provider. |
groups_key |
(none) | [Required] The key containing a list of groups allocated to the user in the signed JWT token. |
username_key |
(none) | [Required] The key containing the preferred username allocated to the user in the signed JWT token. |
user_identifier_key |
(none) | [Required] The key containing the unique ID allocated to the user in the signed JWT token. |